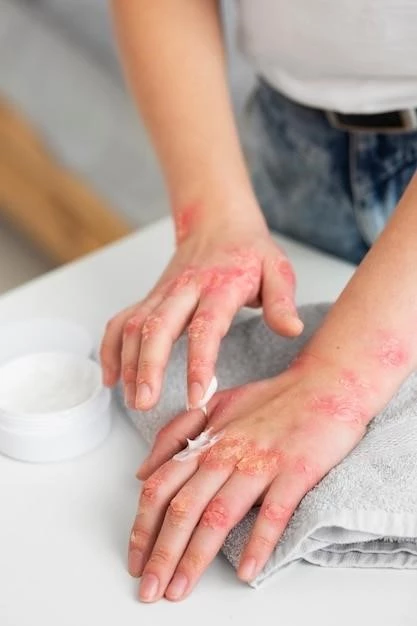
Understanding Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis, also known as erythroderma, involves widespread skin inflammation resulting in rash, peeling, erythema, and scaling. This section provides an overview of the disease, its causes, symptoms, and potential complications.
Introduction to Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis, or erythroderma, is a rare but severe skin condition characterized by widespread inflammation. The skin becomes red, itchy, and scaly, often shedding in sheets. This condition can be triggered by various factors such as drug reactions, infections, underlying skin conditions, or malignancies. Individuals with exfoliative dermatitis may experience extreme discomfort and be at risk for complications.
Understanding the underlying causes of exfoliative dermatitis is crucial for effective management. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes skin biopsies for histopathology. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and underlying cause, with approaches ranging from topical therapies to systemic medications.
In addition to medical interventions, proper skin care is essential for managing exfoliative dermatitis and improving skin health. By following a tailored skincare routine, individuals can help reduce symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and maintain overall skin integrity. It is important for those with exfoliative dermatitis to work closely with a dermatologist to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the symptoms and underlying triggers of the condition.
While exfoliative dermatitis can be challenging to manage, advancements in treatment, including systemic therapies like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, have shown promise in controlling symptoms and reducing inflammation. In severe cases, phototherapy may also be recommended to help alleviate skin inflammation and promote healing. By understanding the complexities of exfoliative dermatitis and adopting a holistic approach to treatment, individuals can better cope with this skin condition and improve their quality of life.
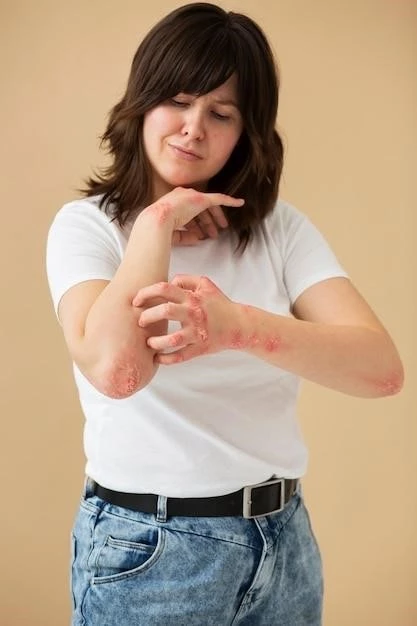

Causes of Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis can be triggered by a variety of factors, including underlying skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, or contact dermatitis. Infections, including HIV, fungal infections, and drug reactions, can also lead to erythroderma. Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, antibiotics, and NSAIDs, have been associated with triggering exfoliative dermatitis.
Other potential causes include malignancies such as lymphoma, metabolic disorders like thyroid dysfunction, and exposure to environmental irritants or allergens. Additionally, emotional stress, alcoholism, and nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate exfoliative dermatitis. Identifying the underlying cause of the condition is crucial for effective treatment and management.
In some cases, exfoliative dermatitis may be linked to autoimmune diseases where the body’s immune system attacks healthy skin cells, leading to inflammation and skin shedding. Understanding the specific triggers and contributors to exfoliative dermatitis can help healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans to address both the symptoms and underlying causes of the condition.
Symptoms of Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis manifests through a range of skin symptoms, including widespread redness (erythema), severe itching, scaling, and peeling of the skin; The affected skin may appear inflamed and feel hot to the touch. In severe cases, the skin can shed in large, flaky sheets, leading to significant discomfort and potential complications.
Individuals with exfoliative dermatitis may experience skin tightness, blisters, oozing, and crusting. The condition often affects large areas of the body, including the face, scalp, trunk, and extremities. Persistent itching can further aggravate the skin and increase the risk of secondary infections.
In some instances, individuals with exfoliative dermatitis may also experience systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, malaise, and swelling of the lymph nodes. These systemic manifestations can indicate the severity of the condition and the body’s inflammatory response to the skin inflammation.
It is essential for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek prompt medical attention from a dermatologist or healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and intervention can help manage the symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the overall quality of life for those affected by exfoliative dermatitis.
Diagnosis of Exfoliative Dermatitis
Diagnosing exfoliative dermatitis requires a comprehensive evaluation by a dermatologist or healthcare provider. The diagnosis is typically based on a thorough medical history, including information about symptoms, potential triggers, and overall health. Physical examination of the skin is crucial to assess the extent of inflammation, redness, scaling, and peeling.
In some cases, skin biopsies may be performed to analyze tissue samples under a microscope (histopathology). Biopsies can help confirm the diagnosis of exfoliative dermatitis and rule out other skin conditions with similar symptoms. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for underlying conditions or factors contributing to the skin inflammation.
It is important for healthcare providers to consider the individual’s medical history, medications, recent infections, and exposure to allergens or irritants when diagnosing exfoliative dermatitis. The differential diagnosis may include psoriasis, eczema, drug reactions, or other forms of dermatitis that share similar clinical features.
Early and accurate diagnosis is key to initiating appropriate treatment and preventing complications associated with exfoliative dermatitis. By collaborating with a skilled dermatologist and undergoing the necessary diagnostic evaluations, individuals can receive timely and effective care to manage their skin condition and improve their overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Exfoliative Dermatitis
The treatment of exfoliative dermatitis aims to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent flare-ups. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the individual’s response to therapy. Topical treatments such as corticosteroids and emollients may be prescribed to soothe the skin, reduce redness, and promote healing.
In cases where exfoliative dermatitis is severe or widespread, systemic medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic agents may be necessary to control the inflammation and skin shedding. These medications are typically prescribed under close medical supervision to monitor for potential side effects and adjust the treatment regimen as needed.
Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet light, may also be recommended for individuals with exfoliative dermatitis. Phototherapy can help reduce skin inflammation, alleviate itching, and improve the overall appearance of the skin. Regular sessions may be required to achieve optimal results.
In addition to medical interventions, maintaining a consistent skincare routine is essential for managing exfoliative dermatitis. Using gentle cleansers, moisturizers, and sunscreens can help protect the skin, prevent dryness, and minimize irritation. Avoiding triggers such as harsh chemicals, excessive heat, and certain fabrics can also help prevent flare-ups.
Individuals with exfoliative dermatitis should work closely with their dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and concerns. By following the prescribed treatment regimen, practicing good skin care habits, and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively manage exfoliative dermatitis and improve the health and appearance of their skin.
Managing Exfoliative Dermatitis⁚ Skin Care
Proper skin care plays a crucial role in managing exfoliative dermatitis and promoting skin health. Individuals with this condition should follow a gentle skincare routine to minimize irritation, reduce inflammation, and protect the skin barrier. Here are some essential tips for managing exfoliative dermatitis through skincare⁚
- Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to gently cleanse the skin without stripping away natural oils.
- Avoid hot water and opt for lukewarm showers or baths to prevent further drying of the skin.
- Pat the skin dry with a soft towel after bathing, avoiding harsh rubbing that can exacerbate irritation.
- Apply moisturizers regularly to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness. Choose moisturizers that are hypoallergenic and fragrance-free.
- Avoid harsh chemicals, fragrances, and additives in skincare products that can irritate the skin and trigger flare-ups.
- Protect the skin from sun damage by using sunscreen with a high SPF and wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses when outdoors.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the skin to prevent further damage and reduce the risk of infection.
- Consult with a dermatologist to determine the most suitable skincare products and treatments for your specific condition.
By incorporating these skincare practices into daily routines, individuals with exfoliative dermatitis can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve the overall health and appearance of their skin. Consistency and gentle care are key in maintaining skin integrity and minimizing discomfort associated with this chronic skin condition.
Potential Complications of Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis can lead to various complications, especially if left unmanaged or if the underlying causes are not addressed. Some of the potential complications associated with exfoliative dermatitis include⁚
- Infection⁚ The compromised skin barrier in exfoliative dermatitis increases the risk of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. These infections can further aggravate skin inflammation and delay healing.
- Dehydration⁚ Severe skin shedding and inflammation can lead to fluid loss, causing dehydration. It is essential to stay well-hydrated and replenish lost fluids to prevent complications.
- Severe Itching⁚ Persistent itching in exfoliative dermatitis can result in skin damage, increased inflammation, and potential scarring. Itching should be managed to avoid further skin complications.
- Psychological Impact⁚ Chronic skin conditions like exfoliative dermatitis can impact mental health and quality of life, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression. Seeking support and professional help is important for overall well-being.
- Skin Discoloration⁚ Prolonged inflammation and skin shedding may result in skin discoloration or changes in pigmentation. These changes can be distressing and affect self-esteem.
- Systemic Effects⁚ In severe cases, exfoliative dermatitis can have systemic effects, including fever, chills, malaise, and weight loss. These systemic symptoms may indicate a more serious condition and require medical attention.
It is crucial for individuals with exfoliative dermatitis to be aware of these potential complications and seek timely medical intervention to address them. By effectively managing the condition, following treatment plans, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can reduce the risk of complications and improve their overall well-being despite the challenges posed by exfoliative dermatitis.
Autoimmune Diseases and Exfoliative Dermatitis
Exfoliative dermatitis has been linked to autoimmune diseases where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation and skin shedding. Autoimmune conditions such as psoriasis, lupus, and dermatomyositis can be associated with the development of exfoliative dermatitis.
In autoimmune-related exfoliative dermatitis, the immune system’s overactive response leads to chronic skin inflammation, redness, and scaling. The presence of autoantibodies targeting skin proteins can contribute to the pathology of exfoliative dermatitis in individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosing and managing exfoliative dermatitis in the context of autoimmune diseases requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the skin symptoms and the underlying autoimmune condition. Treatment strategies may involve immunosuppressive medications, corticosteroids, biologic agents, or other systemic therapies to control inflammation and modulate the immune response.
Individuals with autoimmune-related exfoliative dermatitis may benefit from close monitoring by dermatologists and rheumatologists to ensure a coordinated treatment plan that targets both the skin manifestations and the autoimmune component of the disease. By addressing the autoimmune aspect of exfoliative dermatitis, healthcare providers can help individuals achieve better symptom control and quality of life.
Systemic Treatments for Exfoliative Dermatitis
Systemic treatments play a crucial role in managing exfoliative dermatitis, especially in cases where topical therapies alone may not provide sufficient relief. Systemic medications target the underlying inflammatory processes that drive the skin shedding, redness, and discomfort associated with exfoliative dermatitis.
Corticosteroids⁚ Oral corticosteroids such as prednisone are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in exfoliative dermatitis. These medications can help alleviate symptoms and promote skin healing, but long-term use may be associated with side effects.
Immunosuppressants⁚ Drugs that suppress the immune system, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, or azathioprine, may be used to manage severe cases of exfoliative dermatitis that do not respond to other treatments. These medications help control the immune-mediated inflammation that drives the skin symptoms.
Biologic Agents⁚ Biologic therapies target specific immune pathways involved in the inflammatory response seen in exfoliative dermatitis. Drugs like ustekinumab, adalimumab, or secukinumab may be prescribed in certain cases to achieve targeted and effective control of the skin condition.
When considering systemic treatments for exfoliative dermatitis, healthcare providers carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks of side effects and monitor patients closely for any adverse reactions. Treatment plans are individualized based on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their response to therapy.
It is essential for individuals undergoing systemic treatments for exfoliative dermatitis to adhere to their prescribed regimen, attend regular follow-up appointments, and communicate any concerns or changes in their condition to their healthcare team. By working collaboratively with healthcare providers, individuals can optimize the benefits of systemic therapies while minimizing potential risks, leading to better management of exfoliative dermatitis.
Phototherapy for Exfoliative Dermatitis
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is a treatment option for exfoliative dermatitis that involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light. Phototherapy can help reduce inflammation, alleviate itching, and promote the healing of the skin affected by exfoliative dermatitis.
Types of Phototherapy⁚ There are different types of phototherapy used in the management of exfoliative dermatitis, including⁚
- UVB Therapy⁚ Narrowband UVB or broadband UVB light can help suppress inflammation and promote skin healing in individuals with exfoliative dermatitis.
- PUVA Therapy⁚ Psoralen combined with UVA light (PUVA) is another type of phototherapy that can be effective in treating severe or refractory cases of exfoliative dermatitis.
- Excimer Laser⁚ This targeted form of phototherapy delivers high-dose UVB light to specific areas of the skin affected by exfoliative dermatitis.
Treatment Process⁚ During phototherapy sessions, the affected skin areas are exposed to the appropriate wavelength of light for a specified duration. The frequency and duration of treatment sessions are determined by healthcare providers based on the individual’s response to therapy and skin condition.
Benefits and Considerations⁚ Phototherapy for exfoliative dermatitis can offer significant benefits, including reduced inflammation, itch relief, and overall improvement in skin appearance. However, potential side effects such as sunburn, skin dryness, and long-term UV exposure risks should be considered and discussed with the healthcare team.
Patients undergoing phototherapy for exfoliative dermatitis should follow the recommended treatment schedule, protect their skin from excessive sun exposure, and report any adverse reactions to their healthcare provider. By combining phototherapy with other treatment modalities and skincare practices, individuals can effectively manage exfoliative dermatitis and achieve better skin health.
In conclusion, exfoliative dermatitis, characterized by widespread skin inflammation, redness, peeling, and scaling, poses challenges for those affected. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial in managing this complex skin condition.
From identifying triggers such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or medications to exploring treatment modalities like topical therapies, systemic medications, and phototherapy, a comprehensive approach is needed to address exfoliative dermatitis effectively. Skincare practices play a vital role in alleviating symptoms and maintaining skin health.
Managing potential complications, particularly infections, dehydration, itching, and psychological impact, requires proactive care and attention. For individuals with autoimmune-related exfoliative dermatitis, targeting the immune component is essential for long-term symptom control.
Systemic treatments and phototherapy offer additional options for individuals with severe or refractory exfoliative dermatitis, providing targeted relief and promoting skin healing. Regular monitoring, adherence to treatment plans, and open communication with healthcare providers are key to successful management.
By fostering a collaborative relationship with dermatologists, rheumatologists, and other healthcare professionals, individuals can navigate the complexities of exfoliative dermatitis and work towards improving their quality of life. With proper care, education, and support, individuals can effectively manage exfoliative dermatitis and minimize its impact on daily life.