Introduction to Palmoplantar Keratoderma
Palmoplantar Keratoderma refers to marked thickening of skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet․ This condition can be hereditary or acquired․
Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ also known as keratosis palmaris et plantaris‚ involves marked thickening of the skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet․ It can be hereditary or acquired‚ with various forms and associated symptoms․

Types and Classification of Palmoplantar Keratoderma
Palmoplantar Keratoderma involves marked skin thickening on the palms and soles‚ presenting in hereditary or acquired forms with varied symptoms․
Hereditary Forms
Hereditary Palmoplantar Keratodermas are a group of disorders characterized by hyperkeratotic thickening of the palms and soles․ Different types‚ such as diffuse and focal‚ present with varied associated features and inheritance patterns․
Acquired Forms
Acquired Palmoplantar Keratoderma tends to present more commonly in adulthood and can manifest as thickened skin on the palms and soles․ This form can be diffuse‚ affecting larger areas of the palms and soles‚ or focal‚ localized to pressure points․
Definition and Characteristics
Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ or keratosis palmaris et plantaris‚ involves the marked thickening of the skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet․
Genetic Mutations
Palmoplantar Keratoderma can be attributed to mutations in various genes‚ such as GJB2 or keratin genes‚ leading to abnormal skin protein production and the development of thickened skin on the palms and soles․
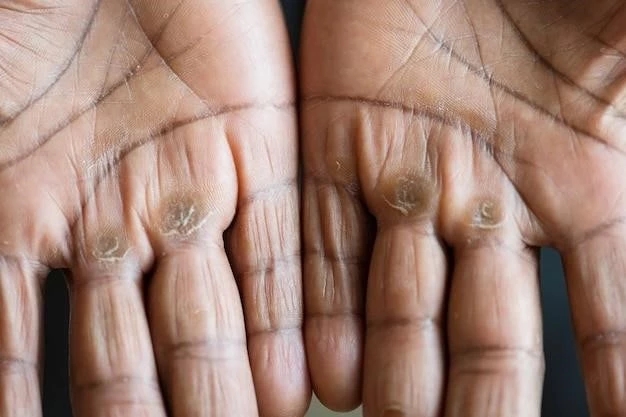
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Palmoplantar Keratoderma presents with thickened skin on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet‚ often hereditary and with diverse forms․
Palmoplantar Keratoderma commonly presents with thickened skin on the palms and soles due to hyperkeratosis‚ often associated with genetic mutations in keratin genes․
Common Signs
Palmoplantar Keratoderma commonly presents with thickened skin on the palms and soles due to hyperkeratosis‚ often linked to genetic mutations․
Diagnosing Palmoplantar Keratoderma involves a thorough medical history review‚ skin examination‚ and potentially genetic testing to identify underlying mutations contributing to the condition․ A dermatologist can provide a comprehensive evaluation to determine the appropriate treatment approach․
To diagnose Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ a comprehensive medical evaluation is required with a detailed history‚ skin examination‚ and likely genetic testing for precise diagnosis and treatment planning․
Medical Management
The treatment approach for Palmoplantar Keratoderma typically involves a combination of emollients‚ keratolytic agents‚ topical steroids‚ and retinoids to manage symptoms and reduce skin thickening․ Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed․
Surgical Interventions
In cases of severe Palmoplantar Keratoderma resistant to medical management‚ surgical interventions like keratolytic techniques‚ dermabrasion‚ and skin grafting may be considered to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life․ Consulting with a dermatologist or a surgeon specialized in skin conditions is essential to explore surgical options․
Medical Evaluation
To diagnose Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ a thorough medical evaluation involving a detailed history‚ skin examination‚ and possibly genetic testing is crucial․ Consulting a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment is recommended․
The prognosis for Palmoplantar Keratoderma varies depending on the specific type and severity of the condition․ While it is a chronic condition with no cure‚ proper management and treatment can help control symptoms and improve quality of life for affected individuals․ Complications may arise from certain forms of Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ necessitating regular medical follow-ups and adherence to treatment plans to address any potential issues․
Possible Outcomes
The prognosis for Palmoplantar Keratoderma varies based on the type and severity‚ with no definitive cure․ Effective management can control symptoms and enhance the individual’s quality of life․
For individuals with Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ it is advisable to maintain proper skin care by regularly moisturizing‚ avoiding harsh chemicals‚ using gentle exfoliants‚ and wearing comfortable footwear to minimize friction․ Seeking advice from a dermatologist for suitable skincare products and routines can be beneficial in managing the condition effectively․
Skin Care Tips
For individuals with Palmoplantar Keratoderma‚ it is essential to maintain proper skin care by using gentle products‚ avoiding harsh chemicals‚ and wearing comfortable footwear to reduce friction on the palms and soles․ Regular moisturizing and exfoliation can help manage the thickened skin effectively․
Recent research on Palmoplantar Keratoderma focuses on genetic mutations in keratin genes‚ including KRT1 and KRT9‚ associated skin manifestations‚ as well as potential surgical techniques and advances in treatment options․ Studies also investigate the complex nature of hereditary and acquired forms‚ aiming to improve diagnostic methods and enhance patient care․
Current Studies
Ongoing research on Palmoplantar Keratoderma focuses on understanding genetic mutations‚ skin manifestations‚ and exploring surgical techniques and treatment advancements․ Studies aim to enhance diagnostic accuracy and care for affected individuals with this condition․