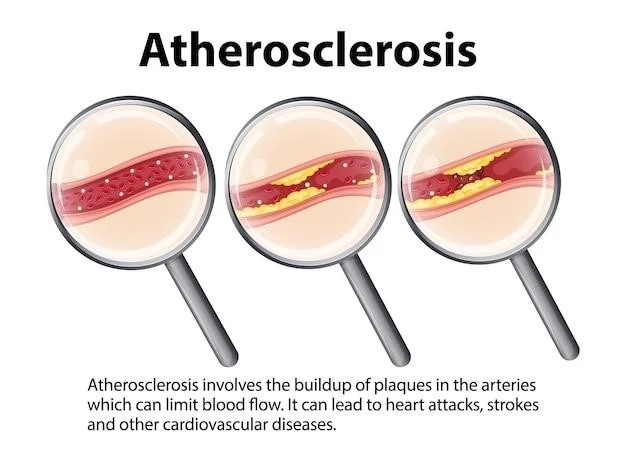
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, also known as Flegel’s disease, is a rare chronic skin disorder characterized by keratinocyte lesions. This dermatological condition has autoimmune origins, leading to persistent hyperkeratotic plaques on the skin.
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, also known as Flegel’s disease, is a rare chronic skin disorder characterized by the development of small, reddish-brown papules and hyperkeratotic plaques on the skin. Typically, these lesions appear on the lower extremities, especially the thighs, and may be asymptomatic or mildly itchy.
The exact cause of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is not well understood, but it is believed to have autoimmune origins. This condition affects the keratinocytes, which are the predominant cells in the epidermis responsible for producing keratin, a tough, fibrous protein that helps form the skin’s structure.
Individuals with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans may experience persistent, slowly spreading plaques that can be challenging to treat. The lesions are usually asymptomatic, but in some cases, mild itching or a burning sensation may occur. The chronic nature of the disease can have a significant impact on the quality of life of those affected.
Diagnosis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is often based on clinical presentation, and a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the histopathological changes associated with the condition. Treatment options for this rare skin disorder aim to manage symptoms and may include topical therapies, phototherapy, or systemic medications.
Research into Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is limited due to its rarity, but advances in understanding the pathophysiology of the disease and developing more targeted treatments are ongoing. Through continued research efforts, there is hope for improved management strategies and potentially better outcomes for individuals living with this challenging dermatological condition.
Understanding the Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans involves an autoimmune response that leads to the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis. This results in the formation of hyperkeratotic papules and plaques on the skin, particularly in areas such as the thighs.
Researchers believe that an autoimmune reaction triggers the immune system to target the keratinocytes, causing them to overproduce keratin and form the characteristic lesions seen in Flegel’s disease. The exact mechanism by which this autoimmune response is initiated in Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is still not fully understood.
Histopathological examination of skin biopsies from individuals with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans reveals hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. These findings support the hypothesis of an autoimmune etiology underlying the development of this dermatological condition.
Moreover, abnormalities in keratinocyte differentiation and function may contribute to the pathogenesis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Dysregulation of signaling pathways that control keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation could play a role in the persistent hyperkeratotic plaques observed in this disease.
Further research is needed to elucidate the specific immune pathways and molecular mechanisms involved in the pathophysiology of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. By deepening our understanding of the disease at a cellular and molecular level, novel targeted therapies may be developed to effectively manage this challenging dermatological condition.
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel typically presents with the development of small, reddish-brown papules and hyperkeratotic plaques on the skin, particularly on the lower extremities such as the thighs. These lesions are often asymptomatic but may cause mild itching or a burning sensation in some cases.
The skin manifestations of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans are characterized by their persistent nature, slowly spreading over time and forming well-demarcated plaques. The hyperkeratotic papules may vary in size and number, giving the skin a rough texture and an appearance resembling “spiny orange peel,” which is a hallmark of this rare dermatological condition.
Individuals affected by Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans may experience emotional distress and a negative impact on their quality of life due to the visibility of the skin lesions and the chronic nature of the disease. The asymptomatic nature of the lesions can lead to delayed diagnosis, as patients may not seek medical attention until the plaques become more pronounced.
In some cases, patients with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans may report pruritus or a sensation of heat in the affected areas. The clinical presentation of this condition may vary among individuals, with some experiencing more severe symptoms than others. Close monitoring and regular dermatological evaluation are essential for managing the symptoms of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis and Histopathology
Diagnosing Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel often involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s clinical presentation and may require a skin biopsy for histopathological analysis. Dermatologists typically examine the characteristic hyperkeratotic plaques and reddish-brown papules on the skin to establish a diagnosis.
A skin biopsy from a lesion of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans reveals histopathological changes that are indicative of the disease. Features commonly seen include hyperkeratosis, epidermal acanthosis, and a mild perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate in the dermis. These findings help confirm the diagnosis of this rare chronic skin disorder.
The histopathological examination is crucial for distinguishing Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans from other skin conditions with similar clinical presentations; The presence of specific pathological changes in the epidermis and dermis, along with the characteristic distribution of lesions on the skin, aids in differentiating this unique dermatological disorder from other entities;
In addition to the histopathological analysis, dermatologists may perform other diagnostic tests, such as immunological studies, to further investigate the autoimmune nature of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Collaborative efforts between dermatologists and pathologists are essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of this rare skin disorder.
Early and accurate diagnosis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is crucial for implementing timely treatment strategies and addressing the potential emotional and physical impact of the disease on the individual. Continued research into the diagnostic criteria and histopathological features of this condition is necessary to enhance our understanding and improve patient care.
Treatment Options
The management of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel focuses on alleviating symptoms and controlling the progression of the disease. While there is no curative treatment for this chronic skin disorder, various therapeutic options aim to improve the quality of life of affected individuals.
Topical therapies, such as keratolytic agents and corticosteroids, may be prescribed to reduce hyperkeratosis and inflammation in the affected skin areas. These topical treatments can help soften the plaques and alleviate itching or discomfort associated with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans.
Phototherapy, including ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy or psoralen plus ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, has shown effectiveness in some cases of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Phototherapy works by targeting abnormal immune responses and keratinocyte proliferation, helping to improve skin lesions and reduce symptoms.
In cases where topical and phototherapy treatments are ineffective, systemic medications, such as retinoids or immunosuppressants, may be prescribed to manage the symptoms of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. These systemic agents target specific pathways involved in the autoimmune response and keratinocyte dysfunction seen in this skin disorder.
Multidisciplinary care involving dermatologists, immunologists, and other healthcare professionals is essential in developing individualized treatment plans for patients with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. Regular follow-up visits and monitoring of the skin condition are crucial to assess treatment response and adjust therapy as needed.
Research into novel therapeutic approaches, including immune-modulating agents and targeted biologics, holds promise for advancing the treatment of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. By exploring new treatment modalities and enhancing existing therapies, healthcare providers can better support individuals living with this challenging dermatological condition.
Prognosis and Long-term Effects
The prognosis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel varies among individuals and may depend on the severity of symptoms, response to treatment, and the presence of comorbidities. While this chronic skin disorder is not life-threatening, it can significantly impact the quality of life of affected individuals.
Long-term effects of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans can manifest as persistent hyperkeratotic plaques on the skin, leading to cosmetic concerns and emotional distress. The visibility of the lesions and the chronic nature of the disease may affect self-esteem and social interactions, contributing to psychosocial challenges.
Individuals living with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans may experience periods of disease exacerbation and remission, requiring ongoing medical care and management. The long-term effects of this rare dermatological condition underscore the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to treatment and support.
While treatment options aim to control symptoms and improve the skin appearance in Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans, the chronic nature of the disease may necessitate long-term therapy and regular follow-up with healthcare providers. Monitoring for potential side effects of medications and assessing treatment response are essential for optimizing long-term outcomes.
Research into the long-term effects and prognosis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is essential for developing comprehensive care strategies and enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by this skin disorder. Continued advances in dermatological research and therapeutic interventions offer hope for better management of the long-term effects of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans.
Research and Advancements in the Field
Ongoing research in the field of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel is focused on elucidating the underlying pathophysiology of this rare skin disorder and exploring novel treatment avenues to improve outcomes for affected individuals. Advances in dermatological research have provided valuable insights into the autoimmune mechanisms driving the development of hyperkeratotic plaques in this condition.
Recent studies have investigated the role of immune dysregulation and aberrant keratinocyte function in the pathogenesis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. By characterizing specific molecular pathways involved in the autoimmune response and keratinocyte proliferation, researchers aim to identify potential therapeutic targets for more tailored treatment approaches.
Furthermore, advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as molecular profiling and genetic studies, have the potential to enhance our understanding of the genetic predisposition and immune factors contributing to Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. By unraveling the genetic and immunological basis of this skin disorder, researchers can pave the way for personalized medicine strategies.

Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of emerging therapies, including biologics targeting key immune mediators or signaling pathways, are underway to address the unmet medical needs of individuals with Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. These innovative treatment modalities hold promise for more effective disease management and improved patient outcomes.
Collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, and industry stakeholders play a critical role in driving advancements in the field of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans. By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations and sharing scientific knowledge, the dermatological community can accelerate progress in diagnosing, treating, and understanding the complexities of this rare skin disorder.
In conclusion, Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans of Flegel, also known as Flegel’s disease, is a rare chronic skin disorder characterized by the development of hyperkeratotic plaques and papules on the skin. This autoimmune condition affects keratinocytes and presents challenges in diagnosis and management.
Understanding the pathophysiology of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans is crucial in elucidating the autoimmune mechanisms underlying the disease. Histopathological changes seen in skin biopsies provide insights into the dysregulated immune responses and keratinocyte dysfunction that drive the development of hyperkeratotic lesions.
The clinical presentation of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may have more pronounced skin manifestations. Early and accurate diagnosis, supported by histopathological analysis, is essential for implementing appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment options for Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans focus on managing symptoms, reducing hyperkeratosis, and improving the quality of life of affected individuals. Topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic medications play a role in controlling the disease and alleviating discomfort associated with skin lesions.
Research and advancements in the field of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans are ongoing, with a focus on understanding the genetic and immunological factors driving the disease and exploring novel therapeutic approaches. Collaborative research efforts aim to advance diagnostic capabilities and enhance treatment outcomes for individuals living with this challenging dermatological condition.
By continuing to investigate the pathogenesis of Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans and developing targeted therapies, the dermatological community strives to improve the long-term prognosis and quality of life for patients affected by this rare autoimmune skin disorder.