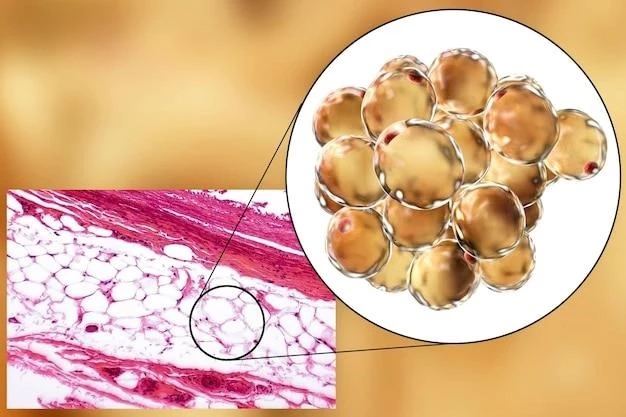
Overview of Roch-Leri Mesosomatous Lipomatosis
Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis is a rare benign autosomal dominant disorder of fat tissue proliferation characterized by the presence of multiple small lipomas in the middle third of the body․
Definition and Characteristics
Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis is a rare benign autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the presence of multiple small painless lipomas, generally 2 to 5 cm in diameter, in the middle third of the body․ These lipomas are typically found in the forearms, trunk, and upper thighs and can be easily removed via local anesthesia․

Background and Related Disorders
The background of Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis involves a condition characterized by multiple lipomas, similar to other lipomatosis-related disorders like Proteus syndrome and Cowden syndrome․
Lipomatosis and Associated Syndromes
Lipomatosis involves the presence of multiple lipomas throughout the body․ Syndromes related to lipomatosis include Proteus syndrome, Cowden syndrome, and disorders like benign symmetric lipomatosis․ Each syndrome presents distinct characteristics in addition to the presence of lipomas․
Disease Definition and Diagnosis
Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis is a rare benign autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the presence of multiple small painless lipomas in specific body areas․ Diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation and imaging studies to confirm the presence of these lipomas․
Clinical Presentation and Diagnostic Criteria
Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis presents with multiple small painless lipomas typically located in specific body areas․ Diagnostic criteria include clinical evaluation and imaging studies to confirm the presence of these lipomas, which are generally non-painful and easily removable․
Research and Findings
Recent research on Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis has highlighted the presence of specific abnormalities like hyperbasophilia and low-grade fat inflammation, warranting further investigation to better understand this rare disorder․
Available Literature and Studies
Recent literature reviews on Dercums disease and Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis have highlighted specific abnormalities like hyperbasophilia and low-grade fat inflammation, suggesting the need for further research to explore these rare disorders․
Treatment and Management
Treatment options for Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis include surgical removal of the lipomas, especially when they are painful or cosmetically bothersome․ Non-surgical interventions may involve close monitoring or pharmacological management to alleviate any associated symptoms․
Surgical Options and Non-Surgical Interventions
Surgical options for treating Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis involve the removal of painful or cosmetically bothersome lipomas․ Non-surgical interventions may include close monitoring or pharmacological management to address symptoms associated with the disorder․
Specific Phenotypes and Metabolic Features
Characterized by the presence of multiple small painless lipomas, Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis can be differentiated from Dercum’s disease by its lack of associated pain and typical locations of fat tissue proliferation․
Differentiating Dercums Disease from Roch-Leri Mesosomatous Lipomatosis
When distinguishing Dercums disease from Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis, it is essential to consider the presence of pain in lipomas, the locations of fat tissue accumulation, and the associated metabolic features that can help in accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies․
Support Resources and Future Directions
Support groups and research opportunities are vital for individuals with Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis to access valuable information, connect with others facing similar challenges, and contribute to ongoing studies for improved understanding and management of this rare disorder․
Support Groups and Research Opportunities
Support groups play a crucial role in providing information and connections for individuals with Roch-Leri mesosomatous lipomatosis․ Additionally, research opportunities are essential for further understanding this rare disorder and developing improved management strategies․