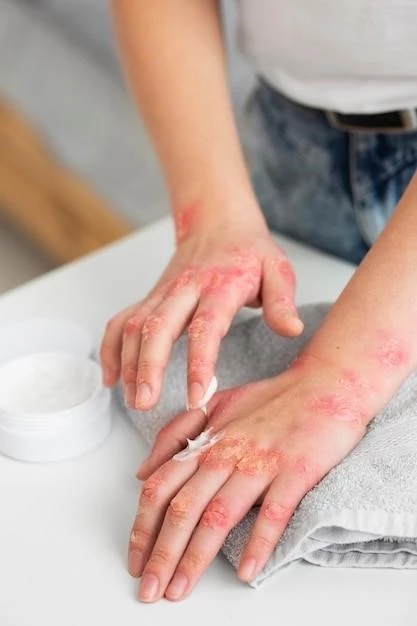
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, can be caused by a combination of factors such as genetics, a compromised skin barrier, abnormal immune response, environmental triggers, and allergens. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with a family history of eczema increasing the likelihood of developing the condition. Additionally, abnormalities in the skin barrier allow moisture to escape and irritants to enter, leading to inflammation. An overactive immune response in individuals with atopic dermatitis can cause the skin to become red, itchy, and inflamed. Environmental factors like harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and seasonal changes can exacerbate symptoms. Allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and certain foods can trigger flare-ups in susceptible individuals. Understanding these various causes is essential in effectively managing and treating atopic dermatitis.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis presents with a range of symptoms that can vary in severity from mild itching and redness to intense inflammation and skin thickening. Common symptoms include dry, itchy skin, red or inflamed patches, small bumps that may leak fluid when scratched, thickened or scaly skin, and rough, cracked skin. Individuals with atopic dermatitis may also experience intense itching, which can worsen at night, leading to sleep disturbances. In severe cases, the skin may become infected, resulting in oozing lesions and crusting. The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can impact daily activities, affect self-esteem, and lead to emotional distress. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective management of the condition.
Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
Managing atopic dermatitis involves a multifaceted approach. Topical treatments such as emollients, corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors can help reduce inflammation and relieve itching. For moderate to severe cases, systemic medications like oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be prescribed. Phototherapy using ultraviolet light under medical supervision can also be beneficial. Proper skincare practices including gentle cleansers, moisturizers, and avoiding triggers are essential. In some cases, wet wrap therapy or bleach baths may be recommended. It is crucial to work with a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and symptoms. Ongoing management and regular follow-ups are important to control the condition effectively.
Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis Flare-ups
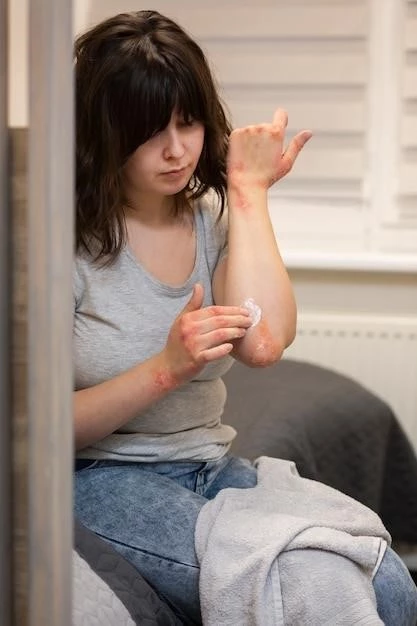

Preventing flare-ups of atopic dermatitis involves identifying and avoiding triggers that exacerbate the condition. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine with gentle cleansers and moisturizers can help protect the skin barrier. Avoiding irritants such as harsh soaps, fragrances, and rough clothing is essential. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can reduce flare-ups. Allergy testing to identify and avoid triggers like dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods is beneficial. In children, keeping their skin moisturized, using mild detergents, and dressing them in soft fabrics can prevent flare-ups. Understanding and addressing individual triggers are key to minimizing the frequency and severity of atopic dermatitis episodes.
Atopic Dermatitis in Children
Atopic dermatitis is a common skin condition in children, characterized by dry, itchy skin and red patches. It often appears on the face, scalp, elbows, and knees. Managing atopic dermatitis in children involves gentle skincare practices, regular moisturization, and identifying triggers to avoid flare-ups. Using mild soaps, soft clothing, and keeping their nails short can help prevent itching and skin damage. Pediatric dermatologists may recommend topical treatments like emollients and corticosteroids appropriate for children’s sensitive skin. Minimizing exposure to allergens, maintaining a comfortable indoor environment, and following a consistent treatment plan are crucial in managing atopic dermatitis in children effectively.
Managing Stress with Atopic Dermatitis
Stress management is crucial for individuals with atopic dermatitis as stress can exacerbate symptoms. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress levels. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy work-life balance, and getting an adequate amount of sleep are essential for managing stress. Seeking support from family, friends, or a mental health professional can also be beneficial. Developing coping strategies to deal with stress triggers and practicing self-care activities can improve overall well-being and quality of life for individuals with atopic dermatitis.
Natural Remedies for Atopic Dermatitis
While medical treatments are essential for managing atopic dermatitis, some individuals may seek complementary natural remedies to help alleviate symptoms. Natural remedies like coconut oil, aloe vera, sunflower seed oil, and colloidal oatmeal can provide moisturizing and soothing effects to the skin. Adding essential oils like lavender or chamomile to bath water may help calm irritated skin. Probiotics and omega-3 fatty acids found in foods like yogurt and fish can support skin health. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before trying natural remedies to ensure they are safe and effective for individual needs. Natural remedies can complement conventional treatments but should not replace prescribed medical interventions.
Impact of Diet on Atopic Dermatitis
Diet plays a role in managing atopic dermatitis, with certain foods potentially triggering or worsening symptoms. Common allergenic foods like dairy, eggs, nuts, and gluten may exacerbate inflammation in some individuals. Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall skin health. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish٫ flaxseeds٫ and walnuts have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit individuals with atopic dermatitis. Keeping a food diary to track potential triggers and working with a healthcare provider or dietitian to identify and eliminate problematic foods can help manage symptoms. While diet alone may not cure atopic dermatitis٫ making informed dietary choices can complement other treatment strategies and improve skin condition.