Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome is caused by genetic mutations and environmental factors․
What is Chitty–Hall–Webb Syndrome
Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by intellectual disability, delayed speech development, distinctive facial features, and skeletal abnormalities․ It is named after the three physicians who first described it․ Individuals with this syndrome may also have heart defects and hearing loss․ Understanding the genetic and environmental causes of this syndrome is crucial for developing effective treatment and management strategies․
Background and History
Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome was first described in medical literature in the early 2000s․ Since then٫ researchers have been working to better understand the underlying genetic mutations and environmental factors that contribute to this rare condition․ Early diagnosis and interventions play a vital role in improving the quality of life for individuals affected by this syndrome․ Ongoing research and advancements in medical technology continue to enhance our knowledge and treatment options for Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․

Causes of Chitty–Hall–Webb Syndrome
Genetic mutations and environmental factors contribute to the development of Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
Genetic Mutations
Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the FGFR2 gene․ These genetic mutations affect the normal development of various body systems, leading to the characteristic features and symptoms of the syndrome․ Understanding the specific genetic mutations involved in this syndrome is essential for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans․ Ongoing genetic research plays a significant role in uncovering new insights into the genetic basis of Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
Environmental Factors
While genetic mutations play a primary role in Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome, environmental factors such as exposure to toxins, infections during pregnancy, or maternal stress may also influence the development of this condition․ Research suggests that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental influences contributes to the complexity of this rare syndrome․ Understanding and addressing these environmental factors are crucial for comprehensive management and support for individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
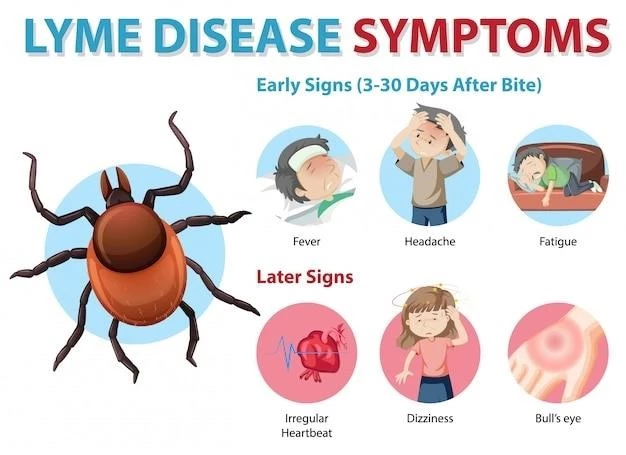
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Chitty–Hall–Webb Syndrome
Distinctive facial features, skeletal abnormalities, intellectual disability, and delayed speech are key traits․
Common Symptoms
Individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome commonly exhibit intellectual disability, delayed speech development, distinct facial features such as a broad forehead and widely spaced eyes, skeletal issues like fusion of cervical vertebrae, heart defects, and hearing loss․ These symptoms vary in severity and can impact overall quality of life․ Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention strategies to support individuals with this rare genetic disorder․
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome often involves a comprehensive evaluation by a medical geneticist or a team of specialists․ This evaluation may include detailed physical examinations to identify characteristic features, genetic testing to confirm mutations in the FGFR2 gene, imaging studies to assess skeletal abnormalities, and cardiac evaluations to detect heart defects․ Additionally, hearing tests and developmental assessments are essential components of the diagnostic process․ Early and accurate diagnosis enables healthcare providers to develop tailored treatment plans and provide appropriate support for individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
Treatment Options for Chitty–Hall–Webb Syndrome
Medical interventions and supportive therapies are key for managing Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions for Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome focus on addressing specific health concerns like heart defects and skeletal issues․ Surgical procedures may be necessary to correct abnormalities․ Additionally, cardiac monitoring and management by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are crucial․ Regular follow-ups and preventive care help manage potential complications․ Each individual with this syndrome may require a personalized medical intervention plan tailored to their unique needs and challenges․
Therapies and Supportive Care
Therapies like speech and occupational therapy are essential for individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome to enhance communication skills and independence․ Physical therapy can address skeletal issues and improve mobility․ Behavioral interventions and educational support play a vital role in managing intellectual disability․ Moreover, psychological counseling and family support services help navigate the challenges associated with the syndrome․ A holistic approach that includes various therapies and supportive care is key to improving the quality of life for individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome․
Prognosis and Life Expectancy of Chitty–Hall–Webb Syndrome
Understanding long-term outlook and factors affecting life expectancy is crucial for managing the syndrome․
Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome varies depending on the severity of symptoms, early intervention, and the presence of associated health issues․ With appropriate medical care, supportive therapies, and family support, individuals can improve their quality of life and achieve milestones to the best of their abilities․ Regular monitoring and individualized care plans play a significant role in maximizing potential and promoting overall well-being․ Continued research and advancements in treatment options further enhance the long-term outlook for individuals with this rare syndrome․
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
Several factors influence the life expectancy of individuals with Chitty-Hall-Webb Syndrome, including the presence of cardiac abnormalities, respiratory issues, and the severity of intellectual disabilities․ Timely access to medical care, management of associated health conditions, and adherence to treatment plans can positively impact life expectancy․ Continuous monitoring by a multidisciplinary healthcare team, proactive interventions, and a supportive environment are essential in optimizing the overall health and longevity of individuals with this rare genetic disorder․