Introduction to Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass‚ micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone sterility‚ and consequent increase in fracture risk.
Definition and Overview
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass and micro-architectural deterioration‚ leading to increased fracture risk. It affects mainly older adults and postmenopausal women‚ weakening bones and making them more prone to fractures‚ particularly in the hip‚ spine‚ and wrist. While often symptomless‚ osteoporosis can significantly impact quality of life‚ mobility‚ and mortality rates. Various factors such as aging‚ hormonal changes‚ and poor nutrition contribute to its development. Understanding the causes and symptoms of osteoporosis is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can be caused by factors such as aging‚ hormonal changes‚ poor nutrition‚ low vitamin D or calcium intake‚ and certain disorders. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention.
Various factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis‚ such as aging‚ hormonal changes‚ genetics‚ inadequate calcium and Vitamin D intake‚ sedentary lifestyle‚ smoking‚ excessive alcohol consumption‚ and certain medications. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and prevention of osteoporosis.
Risk Factors and Contributors
Osteoporosis can result from aging‚ hormonal changes‚ genetic predisposition‚ low calcium or Vitamin D‚ sedentary lifestyle‚ smoking‚ and specific medications.
Recognizing the Disease
Osteoporosis is often referred to as a silent disease due to the lack of symptoms until a bone fracture occurs. It primarily affects older individuals‚ especially postmenopausal women‚ and is prevalent in areas like the hip‚ spine‚ and wrist. Early detection through bone density scans is crucial for timely intervention.
Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
Effective treatments for osteoporosis include medications‚ lifestyle changes‚ calcium and Vitamin D supplementation‚ and weight-bearing exercises. Understanding these options is essential for managing the condition.
Medications and Therapies
Treatment for osteoporosis may involve medications such as bisphosphonates‚ hormone-related therapy‚ denosumab‚ and teriparatide. Additionally‚ lifestyle changes‚ calcium and Vitamin D supplements‚ and weight-bearing exercises play a vital role in managing and improving bone health.
Prevention of Osteoporosis
Preventing osteoporosis involves lifestyle changes such as regular weight-bearing exercises‚ a diet rich in calcium and Vitamin D‚ avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol‚ and getting regular bone density screenings.
Building Stronger Bones
To build stronger bones and reduce the risk of osteoporosis‚ individuals can engage in weight-bearing exercises like walking‚ jogging‚ and resistance training. Consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium‚ Vitamin D‚ and other essential nutrients is crucial for bone health. Additionally‚ avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol intake further supports bone strength and overall well-being.
Types of Osteoporotic Fractures
The most common osteoporotic fractures occur in the hip‚ spine‚ and wrist‚ leading to significant morbidity and mortality among the elderly population.
Common Sites of Fractures
Morbidity and mortality rates are significantly impacted by osteoporotic fractures‚ with hip‚ spine‚ and wrist fractures being prevalent among individuals with weakened bone density. These fractures can lead to severe complications and reduced quality of life.
Osteoporosis significantly reduces the quality of life‚ leading to increased morbidity‚ mortality‚ and disability‚ especially due to fractures in the spine‚ hip‚ and wrist.
Impact of Osteoporosis on Quality of Life
Osteoporosis significantly reduces the quality of life‚ leading to increased morbidity‚ mortality‚ and disability‚ especially due to fractures in the spine‚ hip‚ and wrist.
End Stage Osteoporosis
End-stage osteoporosis‚ characterized by severe bone weakening and increased fracture risks‚ can lead to significant pain‚ mobility issues‚ and reduced quality of life.
Morbidity and Mortality Rates
Osteoporosis significantly impacts morbidity and mortality rates‚ especially with common fractures in the spine‚ hip‚ and wrist‚ leading to increased disability and reduced quality of life.
Researchers have made significant breakthroughs in understanding energy metabolism and bone homeostasis‚ leading to new insights into osteoporosis treatment and prevention.
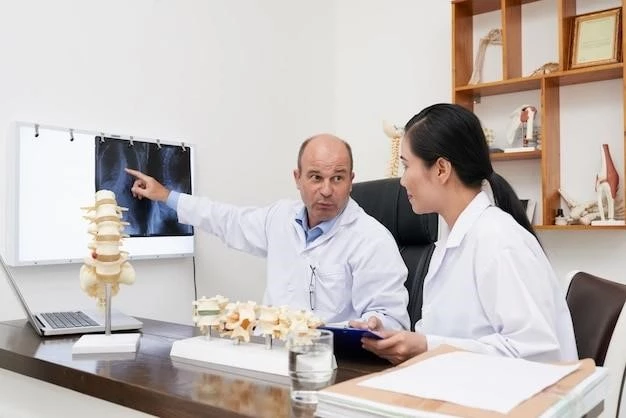

Osteoporosis Research and Breakthroughs
Researchers have made significant breakthroughs in understanding energy metabolism and bone homeostasis‚ providing new insights into osteoporosis treatment and prevention.
Managing Osteoporosis Holistically
Managing osteoporosis holistically involves a combination of nutrition‚ exercise‚ and medical care to strengthen bones‚ improve bone density‚ and reduce the risk of fractures.
Latest Discoveries and Advancements
Researchers have recently made significant advances in understanding the regulation of energy metabolism and bone homeostasis‚ offering promising insights for the treatment and management of osteoporosis.