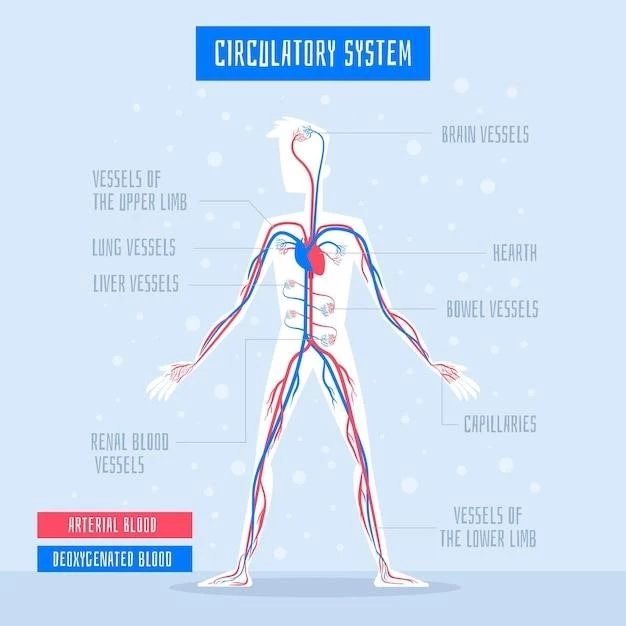
Transposition of the great vessels (TGA) is a complex congenital heart defect that affects blood flow in the heart‚ causing serious symptoms. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial. Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect TGA in yourself or a loved one.
Introduction and Prevalence
Transposition of the great vessels (TGA) is a congenital heart defect affecting the blood flow in the heart. With a prevalence of 3.5/10‚000 live births‚ early detection through obstetric ultrasound is common. This condition involves a discordance between the aorta and pulmonary trunk during cardiac development‚ leading to serious health implications. Understanding the prevalence and early detection methods is crucial for prompt intervention and management.
Definition and Causes
The transposition of great vessels (TGV) is a critical congenital heart defect present from birth. It involves an abnormal switch in the two major arteries carrying blood away from the heart‚ leading to serious health implications. The causes of TGV stem from cardiac development anomalies during fetal life‚ resulting in the aorta and pulmonary artery being transposed in their positions. Understanding these underlying causes is essential for early detection and appropriate management of the condition.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Transposition of the great vessels can lead to symptoms like cyanosis‚ rapid breathing‚ and feeding difficulties in affected individuals. Diagnosing this condition often involves imaging tests and clinical evaluations. Seek medical advice if you observe such symptoms in yourself or a loved one.
Cyanosis and Other Symptoms
Transposition of the great vessels can result in symptoms such as cyanosis‚ where the skin appears bluish due to lack of oxygen‚ along with rapid breathing‚ feeding difficulties‚ and poor weight gain. Becoming familiar with these signs is crucial to seek timely medical evaluation and start appropriate management.
Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing transposition of the great vessels often involves a combination of imaging tests like echocardiograms‚ electrocardiograms‚ and chest X-rays‚ along with clinical evaluations to assess symptoms and medical history. These diagnostic methods help healthcare providers confirm the condition and create a tailored treatment plan. If you suspect any symptoms of transposition of the great vessels‚ it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional promptly for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Treatment Options
Transposition of the great vessels may require treatment such as a balloon atrial septostomy (BAS) or open heart surgery to correct the defect and restore normal blood flow. Prompt medical intervention is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Balloon Atrial Septostomy (BAS)
Balloon atrial septostomy (BAS) is a procedure often used to manage transposition of the great vessels by creating or enlarging a communication between the two atria of the heart. This intervention can help stabilize the circulation in newborns with this condition before definitive treatment is performed. It is vital to follow the guidance of healthcare professionals and consider this option if recommended for your or your loved one’s care.
Open Heart Surgery
Open heart surgery is a common treatment option for transposition of the great vessels. It involves correcting the abnormal positioning of the major arteries to restore proper blood flow. This surgical procedure is crucial for improving the long-term outcomes and health of individuals with this congenital heart defect. Consulting with a skilled cardiac surgeon and healthcare team is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Surgical Procedures and Interventions
Transposition of the great vessels may require surgical interventions like the Mustard or Senning operation or cardiac transplantation to address the defect and ensure proper blood circulation. Consult with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable surgical procedure.
Mustard or Senning Operation
The Mustard or Senning operation is a surgical procedure commonly used to treat complete transposition of the great arteries (TGA). This operation involves redirecting the blood flow to improve oxygenation. Understanding the risks and benefits of this procedure is essential for making informed decisions about managing this congenital heart defect.
Cardiac Transplantation
Cardiac transplantation is a potential treatment option for individuals with transposition of the great vessels‚ especially in cases where other surgical interventions may not be feasible or successful. This procedure involves replacing a damaged heart with a healthy donor heart to address severe heart conditions. Consult with a specialized healthcare team to explore the possibility of cardiac transplantation for managing this congenital heart defect effectively.
Prognosis and Complications
Individuals with transposition of the great vessels may face varying survival rates and potential complications depending on the severity of the condition and the timeliness of treatment. Understanding the prognosis and being aware of possible complications is crucial in managing this congenital heart defect. Consult with healthcare providers for personalized information and guidance.
Survival Rates
Survival rates for individuals with transposition of the great vessels vary depending on factors like the timing of diagnosis‚ the presence of other cardiac defects‚ and the effectiveness of treatment. Prompt intervention and comprehensive care play a vital role in improving outcomes and enhancing life expectancy. Discuss the prognosis with healthcare professionals to better understand the long-term outlook.
Potential Complications
Complications associated with transposition of the great vessels may include heart failure‚ arrhythmias‚ and impaired heart function. Monitoring for these complications and seeking timely medical care is essential for effective management of this congenital heart defect. Discuss possible complications with healthcare providers to be prepared and proactive in your or your loved one’s care.
Special Considerations
Understanding the impact of transposition of the great vessels on infants and children is crucial. Long-term care and monitoring are vital to ensure the best outcomes. Consult with pediatric heart specialists for tailored care plans and ongoing support.
Impact on Infants and Children
Transposition of the great vessels can have a significant impact on infants and children‚ affecting their overall health and development. It is essential to consider the specialized care and monitoring required for young patients with this congenital heart defect. Adhering to treatment plans and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for ensuring optimal outcomes and well-being in infants and children with transposition of the great vessels.
Long-Term Care and Monitoring
For individuals with transposition of the great vessels‚ long-term care and monitoring are essential aspects of managing this congenital heart defect. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers‚ monitoring for potential complications‚ and adherence to treatment plans can help ensure the best outcomes over time. Engage in continuous communication with the medical team to address any concerns and optimize the quality of care for sustained well-being.