Introduction
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin․ It affects millions worldwide, causing discomfort and impacting quality of life․
Overview of Pyrosis as a Disease
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes red, scaly patches on the skin․ It impacts millions globally, leading to physical discomfort and affecting the mental and emotional well-being of individuals․
Causes and Symptoms
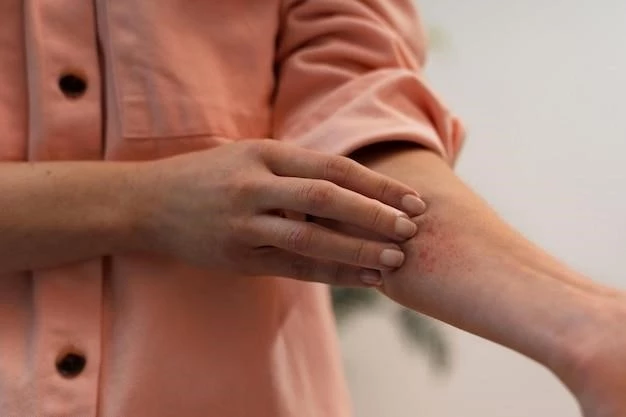
Psoriasis is caused by a malfunction in the immune system, leading to rapid skin cell growth․ Symptoms include red, scaly patches that can be itchy and appear on various parts of the body․
Understanding the Main Causes of Pyrosis
Psoriasis is primarily caused by an autoimmune response where the immune system mistakenly targets skin cells, leading to rapid cell growth․ Genetic and environmental factors also play a role in triggering and exacerbating the condition․
Signs and Symptoms of Pyrosis
Psoriasis manifests as red, scaly patches on the skin, often accompanied by itching․ Common areas affected include knees, elbows, trunk, and scalp․ The condition can cause discomfort, pain, and impact individuals’ quality of life․
Disease Progression
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the development of red, scaly patches on the skin․ The condition can vary in severity and may have cycles of flaring and remission․
Cycles and Flares of Pyrosis
Psoriasis can exhibit cycles of flaring and remission, with symptoms varying in severity over time․ Flares may be triggered by factors like stress, infections, or certain medications, while remission periods offer temporary relief before symptoms reappear․
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of psoriasis involves skin examination and biopsy․ Treatment options include topical therapy, phototherapy, and medications to manage symptoms and improve skin condition․
Diagnosing Pyrosis⁚ Skin Examination and Biopsy
Diagnosing psoriasis involves a thorough skin examination and, in some cases, a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis․ Skin examination helps assess the extent and severity of the condition, while a biopsy aids in determining the type of psoriasis present and ruling out other skin disorders․
Treatment Options for Pyrosis⁚ Topical Therapy, Phototherapy, and Medications
Psoriasis treatment includes topical therapy, phototherapy, and medications․ Topical treatments like corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcineurin inhibitors are commonly used to manage symptoms․ Light therapy (phototherapy) and advanced treatments like biologics may be prescribed for severe cases of psoriasis․
Common Medications for Pyrosis⁚ Corticosteroids, Retinoids, and Calcineurin Inhibitors
Corticosteroids are frequently prescribed for mild to moderate psoriasis․ Retinoids such as Tazarotene are available in gel or cream form, while Calcineurin Inhibitors like tacrolimus can help reduce scaly buildup․ Long-term use of corticosteroids may lead to skin thinning, while retinoids may increase sensitivity to light․
Light Therapy and Advanced Treatments
Psoriasis can be treated with light therapy, also known as phototherapy, which involves controlled exposure to light to alleviate symptoms․ In severe cases, advanced treatments like PUVA and biologics may be recommended to manage psoriasis effectively․
Light Therapy for Pyrosis⁚ Types and Benefits
Light therapy, or phototherapy, is a common treatment for psoriasis that involves controlled exposure to natural or artificial light․ This therapy can help reduce inflammation and improve skin symptoms․ There are different types of light therapy, such as UVB and PUVA, each offering specific benefits for managing psoriasis effectively․
Advanced Treatments like PUVA and Biologics for Severe Psoriasis
For severe psoriasis, advanced treatments like PUVA (psoralen plus ultraviolet A) therapy and biologics are often recommended․ PUVA involves a light-sensitizing medication before UVA exposure, while biologics alter the immune system to improve symptoms rapidly․ These treatments are effective for moderate to severe psoriasis cases that haven’t responded to other therapies․
Potential Risks and Complications
Long-term use of medications for psoriasis can pose risks including skin thinning from corticosteroids, sensitivity to light from retinoids, and potential skin cancer risk from calcineurin inhibitors․ Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to mitigate these risks․
Risks Associated with Long-term Use of Medications for Psoriasis
Long-term use of medications for psoriasis, such as corticosteroids, retinoids, and calcineurin inhibitors, can pose risks including skin thinning, increased sensitivity to light, and potential skin cancer risk․ Regular monitoring and consultation with healthcare professionals are crucial to manage and minimize these potential complications effectively․
Management and Lifestyle Changes
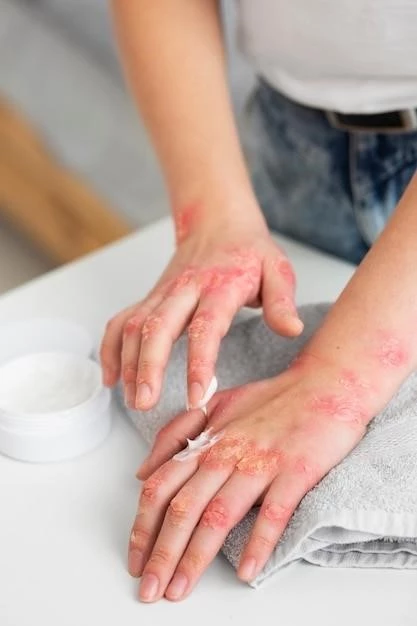
Managing psoriasis involves a combination of treatments like creams, light therapy, and medications․ Lifestyle changes such as stress management, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and sun protection can help improve symptoms and overall well-being․
Self-care Measures to Manage Psoriasis
Self-care for psoriasis management includes adopting healthy lifestyle habits like maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, avoiding triggers, and practicing good skincare․ Additionally, it’s crucial to stay consistent with prescribed treatments and follow up with healthcare providers regularly to monitor progress and address any concerns․
In conclusion, psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing discomfort and impacting overall well-being․ Effective management involves a combination of treatments, self-care measures, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals to minimize risks and complications associated with the condition․
